The main aim of this blog is to give an overview of the process that I followed to pass the GIAC Reverse Engineering Malware (GREM) exam. Hopefully this can help someone who is going through the same journey or planning to start.
You can view my Certificate by visiting the following location.
What is GREM?
Before I get into the resources that I used for exam preparation, let’s talk about GREM a little for those who are new.
The GIAC Reverse Engineering Malware (GREM) cerification is for professionals who protect the organization from the malicious code designed by cyber attackers for their malicious purposes. This certification aims to give the knowledge and skills to reverse engineer malicious software that targets common platforms such as Microsoft Windows, Web browsers, common applications like PDF, Microsoft office etc. This also provides some insights into memory forensics and incident response related process. To get more information about the certification, you can visit their SANS Official page.
There are different packages that one can choose for this certification. I registered for only certification attempt which includes 2 practice test and the certification exam. There are other options also available like live/online training. But if you are on a budget like me, then this will cost a lot. You can find out more about pricing here. Since I took only the exam, I had to prepare before registering. This blog is regarding that preparation.
Course Objectives
The exam objectives or topics that I needed to learn are mentioned on the Official SANS site:
- Malicious Document files: Analyzing scripts (javascript/vbscript) included in the files like microsoft office applications, PDFs etc.
- Packed executable analysis: Techniques used by malware authors to protect the malicious software and how to analyse those executables.
- Analyzing web-based malwares: Tools and techniques used to analyze web-based malwares. Also, in-depth analysis of complex browser scripts.
- Malware Assembly: How to detect malicious characteristics when statically analyzing the windows executable.
- In-Depth analysis of Malicious executables: Analyzing complex executables which have multi-technology being used.
- Memory Forensics: Understanding of windows memory forensics techniques to analyze malware threats. Tool - Volatility
- Code and Behaviour Analysis: Tools and techniques used to do code and behaviour analysis using tools like IDA PRO, debuggers and other useful tools.
- Assembly code concepts: Core concepts to analyze malware’s assembly code for 32-bit or 64-bit architecture.
Preparation
For someone who is very new to cybersecurity world, I would suggest to first learn some basics of it. Like getting good knowledge of assembly language (lots of resources are present out there for this), some security concepts, OS internals etc.
Pre-requisites
- Assembly Language : It goes without saying that knowledge of assembly language is a must for this work. Most of the time for analysis, we would be looking into the assembly code. There are lot resources available on different platforms like coursera, Udemy, edX etc. on this topic.
- Programming Languages : Another obvious thing that is required is basic knowledge of C, C++ concepts. Because many of the windows malwares are PE files that contains lots of programming concepts like loops, pointers etc. Lot of resources are available for this as well.
I was familiar with above mentioned topics as I learned few things in my higher studies and few after starting my career. But they are not enough. Few more things that I focused on are:
- Cybersecurity concepts : Some basic knowledge of security vulnerabilities and how they can be exploited is also critical. I have learned these mostly from corelan site. I started with there stack overflow blog and continued from there.
Resources
To learn all the topics which are mentioned in the course, I have used following resources:
- Books
- Practical Malware Analysis : This is the book that a malware analyst must have come across at some point and is suggested by almost everyone. The best part is that with all the theory, this has the lab content as well. You can understand different concepts with actually doing some practical hands on. They provide the samples on which you can experiment and answer the questions that they ask in the end of the chapter. Great resource to learn static and dynamic malware analysis, techniques used by malware authors to avoid detection, how to analyze packed malwares and much more. Great source of knowledge. Must have!
- Art of Memory Forensics: This book I have used for the memory forensics part of the course. Good way to learn windows internals using the volatility tool.
- Apart from these two books, I have not read anything else, but few more books that are suggested by others are ‘The Malware Analyst’s Cookbook’, ‘The IDA PRO book’, ‘Windows Internals’.
- Cheat Sheets: Many cheat sheets are written by Lenny zeltser (Author and instructor at SANS) out of which few are very helpful for this course.
- Additional Resources: There are many other resources that gives a sense for malware analysis approaches explored in the course, which are mentioned in the SANS official site.
Apart from these, other main resources are other malware researchers. I follow a lot of security researchers on twitter where they share anything new they find. I use to read their blogs for their approach on dissecting a malware and getting around malware’s defences. It’s a huge and helpful community.
Notes
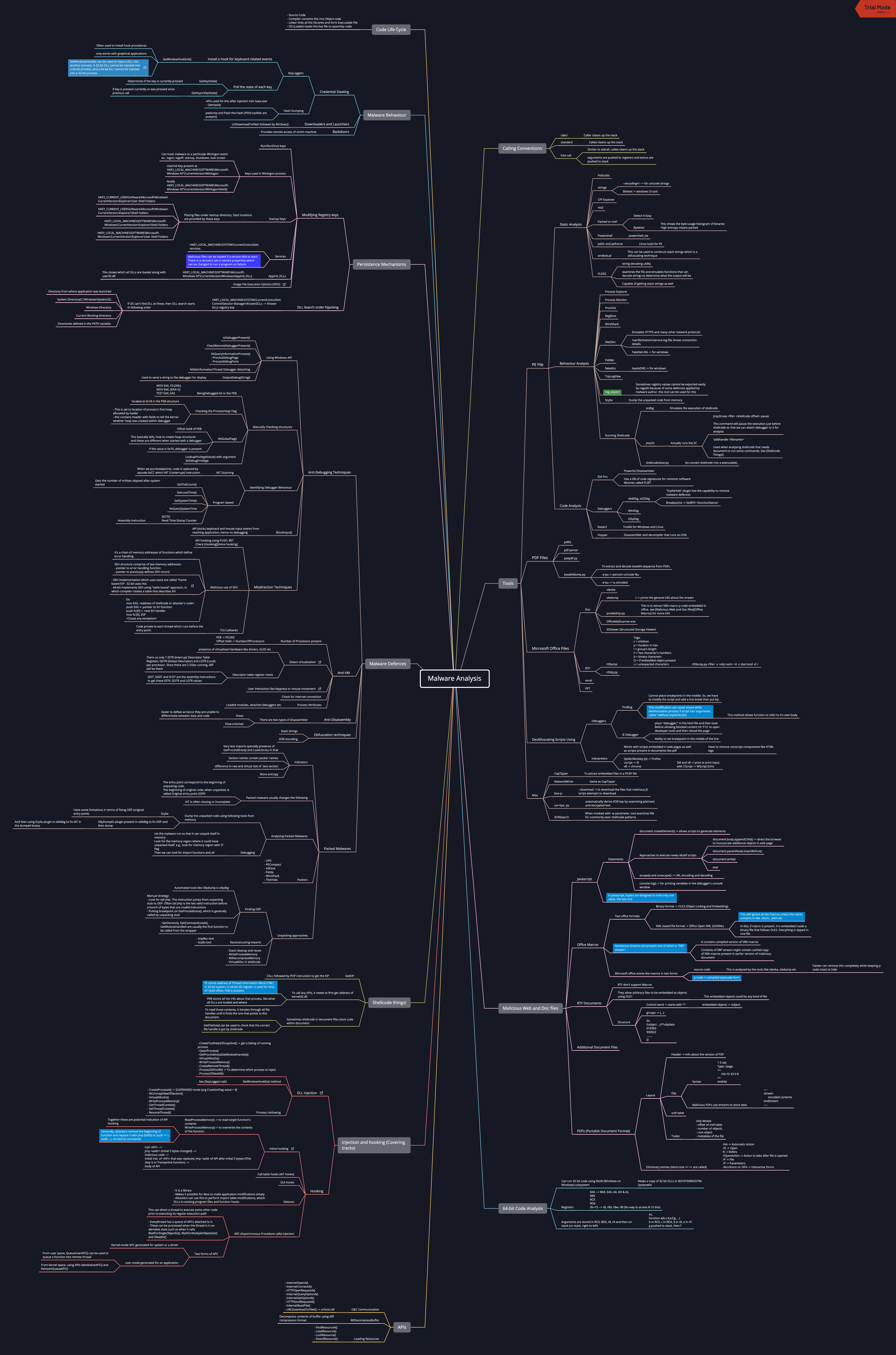
GREM certification exam has open book format. That said, I never relied on books and decided not to take any books or study material. Rather I created notes using xMind app and exported that in PDF format and taken printout of that notes. Frankly speaking, if you practice regularly and understand all the concepts and make the notes thoroughly, books are not required for the exam. They will instead waste a lot of time. But that’s my opinion. In case anyone wants to take books or study material in the exam, make sure that you have done a very good indexing, so that jumping to the location of a particular topic is easy.
The notes that I created looks something like this:
Practice tests
In my opinion, the practice tests are very essential for these exams. They can give some idea about how much prepared you are and what areas to focus more. Also, they can give you look and feel of the actual test. I don’t know whether they are easier or harder than the originl exam but the format is exactly the same. So, it can prepare you for the original exam if given with seriousness.
I got 2 practice tests with the package that I bought and I knew in order to clear the exam, I have to use these two tests wisely. So, after buying the exam, I gave my first practice test. This gave me lot of insights on what are my weak areas on which I have to spend some more time. This way only I got to know that I have to learn more about memory forensics and web based malicious scripts. I calculated rough time I needed to cover these topics and selected my date of exam. After giving some extra time on these topics and having gained some confidence, I gave the second test 1 week before the actual exam and surely my score increased. Then came the D-day and all the hard work and effort gave the awesome result that I was hoping for! I finally cleared the exam with 88% marks.
References
Some usefule links
